The geopolitical landscape of northern Europe and the Arctic has undergone a profound transformation in 2026, driven by NATO’s expansion into Finland and the escalating strategic significance of Greenland. These developments are not isolated; they represent interconnected dimensions of an intensifying security competition between NATO, led by the United States, and Russia. The confluence of Finland’s NATO membership, Greenland’s strategic importance, and Russia’s assertive posture in the Arctic creates a volatile environment with far-reaching implications for global security.
Finland’s accession to NATO in 2024 marked a watershed moment in northern European security. Historically neutral and non-aligned, Finland’s decision to join the alliance was largely catalyzed by the evolving threat perception stemming from Russia’s assertive actions in Ukraine and across the Baltic region. By 2026, Finland’s membership has not only expanded NATO’s territorial footprint but also introduced a new strategic frontier along the extensive Finnish-Russian border, which extends over 1,300 kilometers. This shift complicates Moscow’s calculus, as the increased NATO presence directly abuts Russian territory, heightening the potential for friction and miscalculation.
Finland’s integration into NATO is emblematic of the alliance’s broader strategy to consolidate its northern flank, thereby reinforcing collective defense mechanisms in an area increasingly vulnerable to geopolitical contestation. The move aligns with NATO’s prioritization of Arctic security, reflecting the region’s growing salience as climate change accelerates ice melt, opening new maritime routes and access to untapped natural resources. In this context, Finland’s role is pivotal; its advanced military capabilities, familiarity with Arctic conditions, and strategic location augment NATO’s ability to project power and maintain situational awareness in the High North.
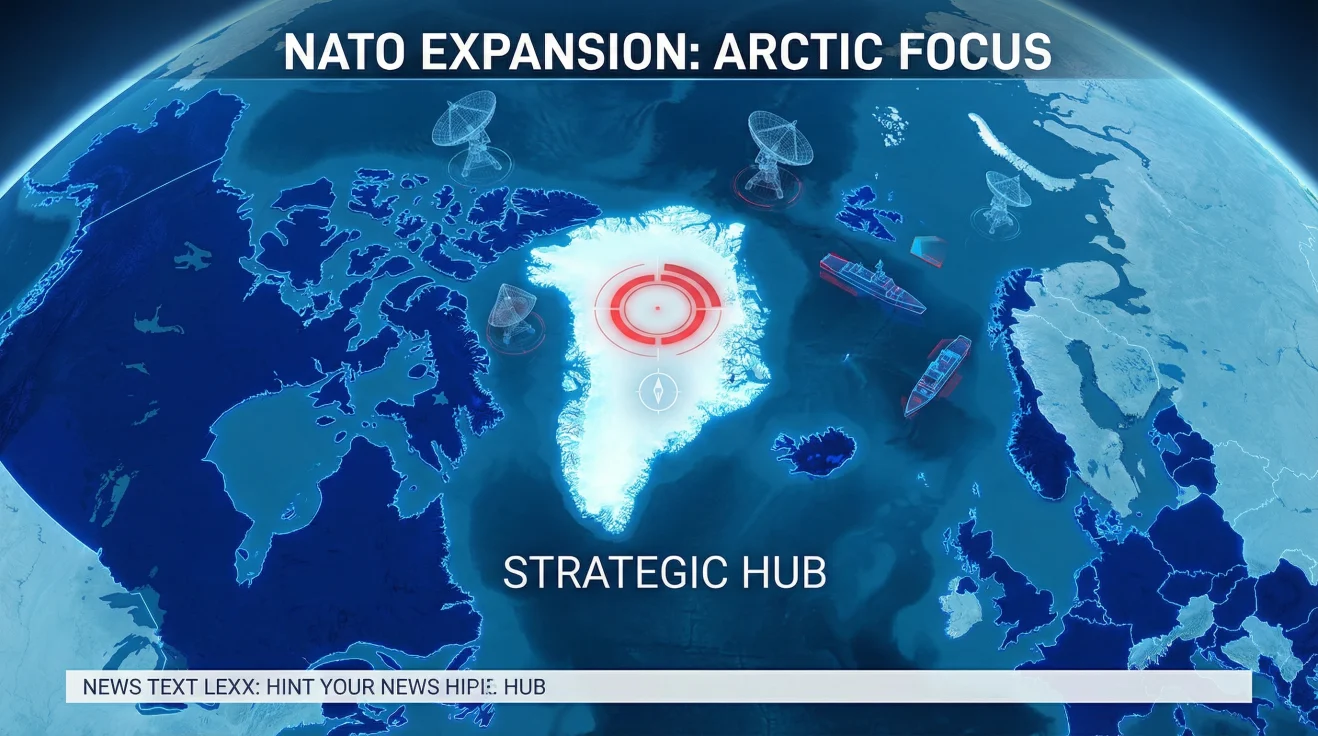
Embedded in this Arctic security framework is Greenland, whose importance has surged dramatically over the past decade. Greenland, an autonomous territory within the Kingdom of Denmark, occupies a critical geographic position between North America and Europe, straddling key transatlantic sea lanes and air routes. Its vast ice sheet conceals substantial mineral wealth, including rare earth elements vital for modern technologies and defense industries. Moreover, Greenland’s proximity to both the North Pole and the North Atlantic makes it an indispensable asset for monitoring and controlling Arctic access.
Greenland’s strategic value has attracted heightened attention from global powers, especially the United States and Russia, each intent on securing influence in this increasingly contested space. The U.S. maintains a significant military presence on the island, including the Thule Air Base, which functions as a crucial early-warning site against missile threats and a hub for satellite communications. This presence underscores Greenland’s role in the broader U.S. defense posture and its commitment to countering Russian advances in the Arctic.
Meanwhile, Russia’s ambitions in the Arctic are manifest in its efforts to enhance military infrastructure along its northern coast, expand its Northern Fleet’s capabilities, and assert control over the Northern Sea Route. These developments pose direct challenges to NATO and U.S. interests in the region, underscoring the strategic contest over access, surveillance, and resource exploitation. Greenland, by virtue of its location and resources, sits at the nexus of these competing agendas, rendering it a critical arena for geopolitical rivalry.
As NATO fortifies its northern presence through Finland and enhances cooperation with Greenlandic authorities, the alliance confronts a complex set of security dilemmas. The expansion has elicited vehement responses from Moscow, which perceives these moves as encirclement and a direct threat to its national security. Russia’s military doctrine has accordingly adapted, emphasizing rapid deployment capabilities along its Arctic frontier and the development of asymmetric tools to counter NATO’s technological advantages.
“Greenland’s evolving role in Arctic security is a strategic chess piece in the broader US-Russia rivalry, underscoring the island’s newfound geopolitical leverage in 2026.”
The intensification of US-Russia tensions around Greenland and the Arctic is further complicated by the island’s internal political dynamics. Greenland’s government has increasingly asserted its aspirations for greater autonomy, seeking to leverage its strategic importance to negotiate enhanced economic and political concessions from Denmark and its allies. The ongoing Greenland sovereignty debate reflects these ambitions and adds a layer of complexity to international negotiations, as the island navigates its dual role as a self-governing entity and a strategic asset within a NATO framework.
In this regard, Greenland’s sovereignty discourse intersects with broader security concerns. The island’s push for increased control over its resources and foreign policy decisions challenges existing defense arrangements and compels the United States and NATO to recalibrate their engagement strategies. This recalibration involves balancing respect for Greenlandic self-determination with the imperatives of collective security in a theater marked by intensifying great power competition.
Finland’s NATO membership and Greenland’s strategic prominence collectively contribute to a heightened security architecture in the Arctic and North Atlantic. The alliance’s enhanced capabilities in these regions serve as a deterrent to Russian expansionism but also risk escalating tensions through military buildups and strategic signaling. The potential for miscommunication or inadvertent confrontations in this fragile environment remains a persistent concern among defense analysts and policymakers.
Moreover, environmental changes are accelerating the pace at which the Arctic transforms into a viable theater for commercial and military activities. Melting ice is opening new shipping routes such as the Northwest Passage and the Northern Sea Route, shortening transit times between major markets and intensifying competition over control and access. Greenland’s ice sheet, a barometer of climate change’s global impact, epitomizes this dual challenge where environmental and security concerns converge.
The United States has responded by deepening its Arctic engagement, increasingly viewing Greenland as a linchpin in its strategy to maintain strategic superiority. Investments in infrastructure, joint military exercises with Denmark and NATO partners, and enhanced intelligence-sharing mechanisms underscore Washington’s commitment to safeguarding this critical region. Greenland’s potential to serve as a forward base for missile defense and surveillance capabilities further elevates its role in the alliance’s long-term strategic calculus.
Russia, for its part, continues to emphasize diplomatic and military initiatives to assert its sovereignty claims and secure access to Arctic resources. This includes the deployment of advanced radar systems along the Kola Peninsula, increased submarine patrols, and assertive naval exercises aimed at demonstrating control over the Arctic maritime domain. The juxtaposition of these efforts with NATO’s northern expansion, particularly through Finland and Greenland, crystallizes a renewed security dilemma reminiscent of Cold War-era rivalries but compounded by contemporary technological and environmental factors.
“The strategic interplay between NATO’s northern expansion and Greenland’s rising geopolitical profile underscores a new era of Arctic competition, with profound implications for global security in 2026 and beyond.”
The NATO expansion debate, when viewed through the lens of Finland and Greenland, reveals a multifaceted security challenge that extends beyond mere membership lists to touch upon fundamental questions about the nature of collective defense, the limits of alliance solidarity, and the management of great power competition in the 21st century. As the alliance faces an increasingly uncertain security environment marked by hybrid threats, cyber warfare, and shifting geopolitical alignments, its approach to expansion will significantly shape the future of Euro-Atlantic security.
In this context, the Arctic and its adjacent regions will remain critical arenas where NATO’s strategic posture and expansion policies intersect. The alliance’s ability to integrate new members with Arctic interests and capabilities, while managing Russia’s assertiveness, will have profound implications for regional stability. Moreover, developments in related geopolitical arenas, such as the Greenland sovereignty discussions, underscore the need for NATO to adapt to a changing security environment that transcends traditional European theaters.
Ultimately, the NATO expansion debate is emblematic of the broader challenges facing the alliance as it navigates an era of renewed great power rivalry. It demands a careful balancing act: honoring commitments to potential new members and the principles of collective security, while managing the risks of escalation and fostering internal unity. The decisions made in this arena will reverberate across global geopolitics, influencing the trajectory of East-West relations, the security architecture of Europe and the Arctic, and the enduring relevance of NATO itself.